Introduction:
All directly welded parts to the pressure parts like lifting lugs, support lug, trunnion etc. are need to be checked for WRC 107/537. All related calculations are carried out in PV Elite once given proper inputs. In some cases, it is not possible to build such directly welded parts in PV Elite due to software constrain. For example, adding lifting lug on top dish end of vertical equipment is not possible in PV Elite. In those cases, it is mandatory to perform WRC calculations by any other means. This article will help to perform such calculations with analytical solutions followed by CodeCalc calculations.
Inputs:
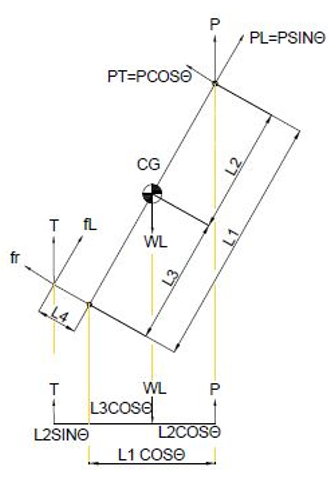
Consider an equipment with top 2:1 ellipsoidal dish end with directly welded lifting lugs. All necessary input data is given below.
| VESSEL OD | Dm | 219.1 | MM |
| VESSEL THICKNESS | t | 6.16 | MM |
| VESSEL WEIGHT | WL | 304.7 | KG |
| VESSEL CG HEIGHT | L3 | 1190.515 | MM |
| DESIGN LENGTH T-T | L1 | 2105.9 | MM |
| CG TO TOP | L2 | 915.385 | MM |
| TAILING LUG OFFSET | L4 | 109.55 | MM |
Solution:
To consider the maximum force acting on equipment, vessel is considered to be lifted from horizontal position to vertical. At all lifting positions forces acting on lifting and tailing lugs are calculated as given below and maximum of acting force is taken for the analysis.
Lifting lug forces:
Maximum transverse load per lug PT = P cosθ / N
Maximum longitudinal load per lug PL= P sinθ / N
Where, N = number of lugs
Tailing lug forces:
Maximum radial load on a lug PR = T sinθ
Maximum longitudinal load on a lug fL= T cosθ
| LIFTING ANGLE θ | TAILING LOAD T (KG) | LIFTING LOAD P (KG) |
| 5 | 131.8458372 | 172.8541628 |
| 10 | 131.2420611 | 173.4579389 |
| 20 | 129.9847735 | 174.7152265 |
| 30 | 128.5839955 | 176.1160045 |
| 40 | 126.9063811 | 177.7936189 |
| 50 | 124.7141611 | 179.9858389 |
| 60 | 121.4986062 | 183.2013938 |
| 70 | 115.8832583 | 188.8167417 |
| 80 | 102.2730061 | 202.4269939 |
| 90 | 1.55963E-13 | 304.7 |
| MAX | 131.8458372 | 304.7 |
| LIFTING LOAD COMPONENT | |||
| MAX TRANSVERSE LOAD PER LUG | PTmax | 1.86651E-14 | KG |
| MAX LONGITUDINAL LOAD PER LUG | PLmax | 304.7 | KG |
| TAILING LOAD COMPONENT | |||
| MAX TRANSVERSE TAILING LOAD | fLmax | 131.344124 | KG |
| MAX LONGITUDINAL TAILING LOAD | frmax | 11.49112187 | KG |
Therefore, 304.7kg force is taken for WRC analysis and its components acting on lug are calculated as given
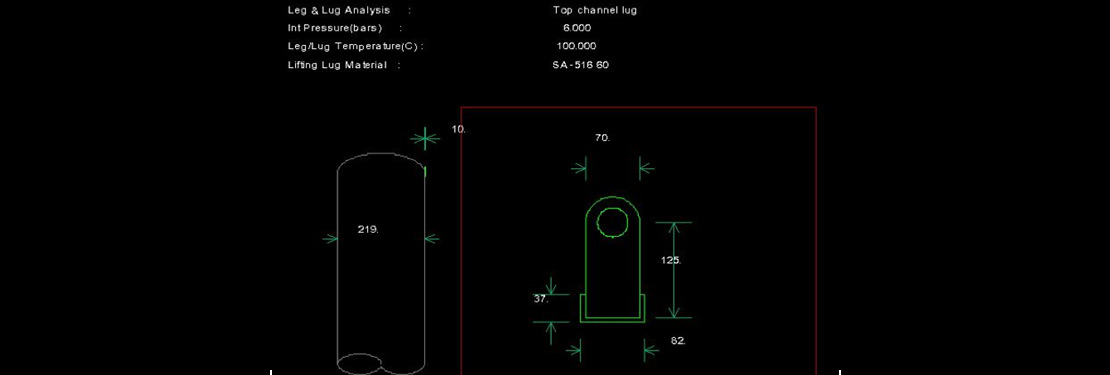
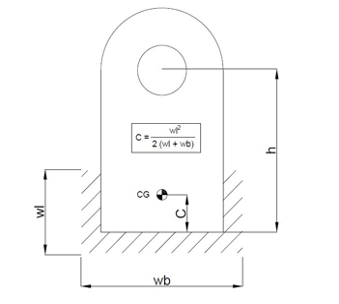
| h | 125 | mm |
| wl | 37 | mm |
| wb | 82 | mm |
| C | 5.752101 | mm |
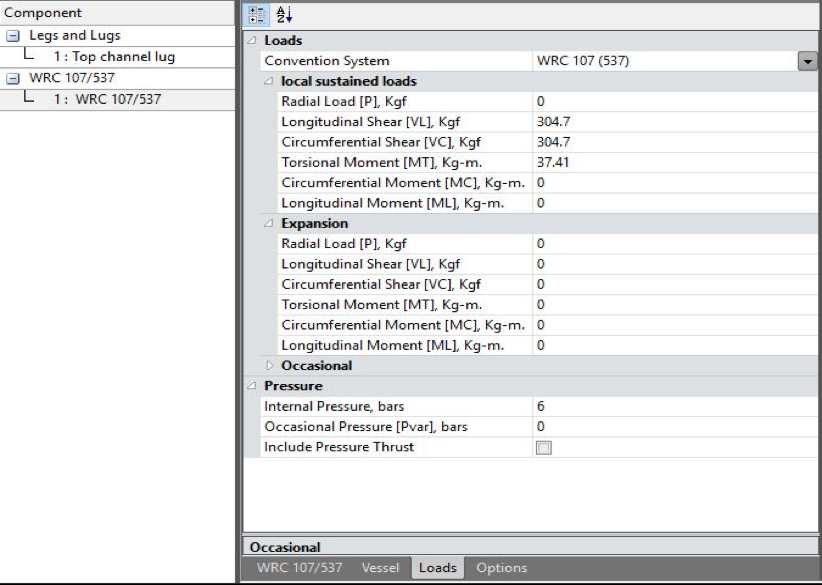
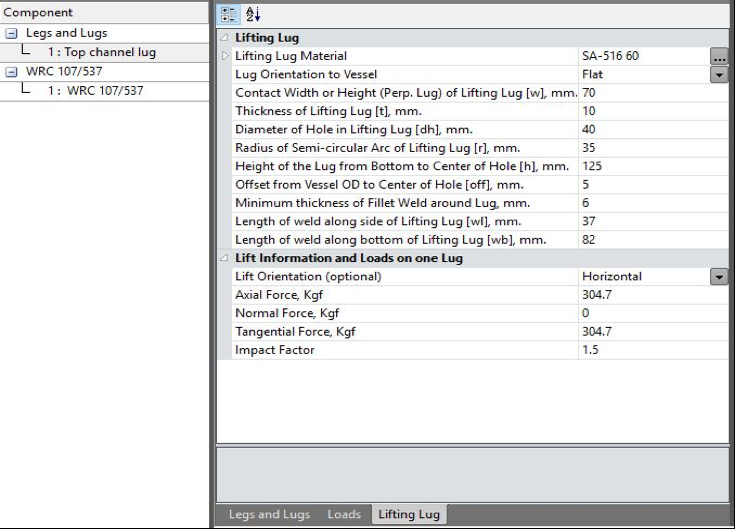
| Radial load acting on lug | Prad | 0 | kgf |
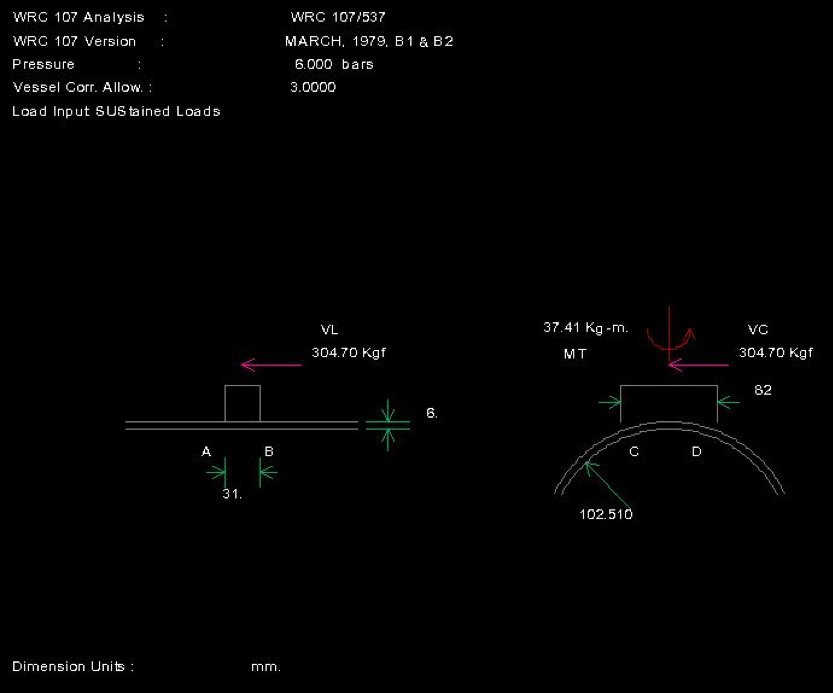
| Longitudinal shear force acting on lug | VC | 304.7 | kgf |
| Circumferential shear force acting on lug | VL | 304.7 | kgf |
| Circumferential moment | MC | 0 | kg-m |
| Longitudinal moment | ML | 0 | kg-m |
| Torsional moment | MT | 36.33483487 | kg-m |
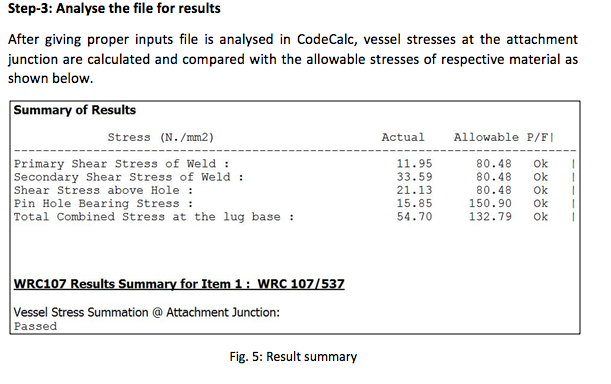
Thus after calculation of forces and moments acting on lifting lug, WRC 107/537 analysis is carried out in CodeCalc in following steps
Step-1: Input lifting lug data in CodeCalc
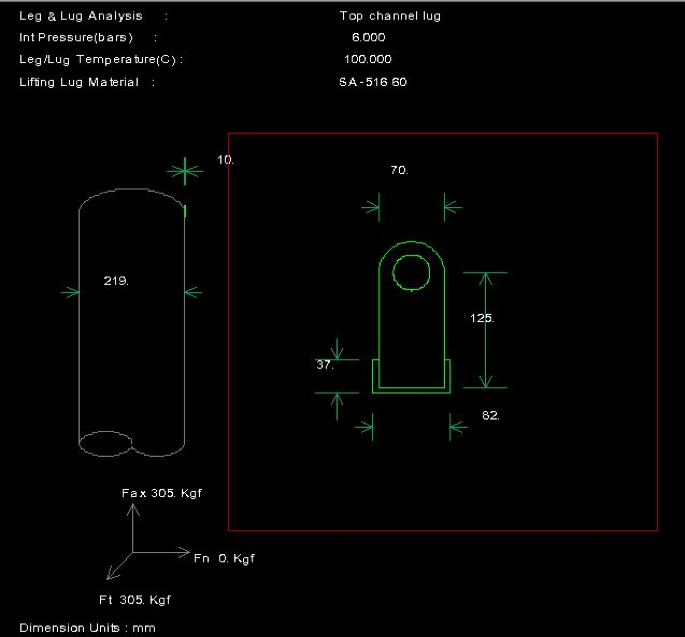
Step-2: Input WRC 107/537 data in CodeCalc